Deep learning for NeuroImaging in Python.
Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the gallery for the big picture.
- class nidl.volume.transforms.augmentation.intensity.random_noise.RandomGaussianNoise(mean: float | tuple[float, float] = 0.0, std: tuple[float, float] = (0.1, 1.0), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
VolumeTransformAdd Gaussian noise to input data with random parameters.
The input data can have any shape with type
np.ndarrayortorch.Tensor. The output has consistent type and shape with the input.- Parameters:
mean : float or (float, float), default=0.0
Mean
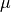 of the Gaussian distribution from which the noise
is sampled. If two values
of the Gaussian distribution from which the noise
is sampled. If two values 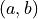 are given, then
are given, then
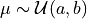 .
.std : (float, float), default=(0.1, 1.0)
Range of the standard deviation
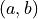 of the Gaussian
distribution from which the noise is sampled
of the Gaussian
distribution from which the noise is sampled
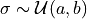 .
.kwargs : dict
Keyword arguments given to base
nidl.transforms.Transform.
Follow us
