Deep learning for NeuroImaging in Python.
Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the gallery for the big picture.
- class nidl.volume.transforms.augmentation.spatial.random_flip.RandomFlip(axes: int | str | tuple[int | str, ...] = 0, flip_probability: float = 1.0, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
VolumeTransformReverse the order of elements in a 3d volume along the given axes.
It handles a
np.ndarrayortorch.Tensoras input and returns a consistent output (same type and shape). Input shape must be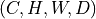 or
or 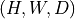 (spatial dimensions).
(spatial dimensions).- Parameters:
axes : int, str or tuple of int or str, default=0
Index in (0, 1, 2) or tuple of indices of the spatial dimension along which the input volume might be flipped. Anatomical labels could be used as well such as “LR” (Left-Right), “AP” (Antero-Posterior) or “IS” (Inferior-Posterior). In that case, RAS-formatted affine matrix specifying volume orientation must be provided when the transformation is called. Check Nibabel documentation on image orientation.
flip_probability : float, default=1.0
Per-axis probability to flip the volume.
kwargs : dict
Keyword arguments given to base
nidl.transforms.Transform.
Notes
Current implementation always returns a new tensor/array without sharing memory with the input data.
- apply_transform(data: ndarray | Tensor, affine: ndarray | None = None) ndarray | Tensor[source]¶
Flip the volume along random axes.
- Parameters:
data : np.ndarray or torch.Tensor
Input volume with shape
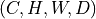 or
or 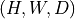 .
Channel dimension will never be flipped.
.
Channel dimension will never be flipped.affine : np.ndarray of shape (4, 4) or None, default=None
Affine transformation matrix of the input data in RAS format defining orientation of the input image. This is typically given by Nibabel in this format. This is used only if anatomical labels are provided in the flipped axes (“LR”, “AP” or “IS”) and ignored otherwise. If None, the identity matrix is used, assuming RAS orientation.
- Returns:
data : np.ndarray or torch.Tensor
Flipped volume with same type and shape as the input.
- get_index_from_anat_label(axis: str, affine: ndarray)[source]¶
Returns the axis index corresponding to a given anatomical label.
- Parameters:
axis : {‘LR’, ‘AP’, ‘IS’}
Anatomical axis label:
‘LR’ for Left-Right (X axis)
‘AP’ for Anterior-Posterior (Y axis)
‘IS’ for Inferior-Superior (Z axis)
affine : np.ndarray
4x4 affine matrix defining the orientation of the volume.
- Returns:
int
The index (0, 1, or 2) in voxel space corresponding to the requested anatomical axis.
Follow us
