Deep learning for NeuroImaging in Python.
Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the gallery for the big picture.
- class nidl.volume.transforms.preprocessing.intensity.rescale.RobustRescaling(out_min_max: tuple[float, float] = (0, 1), percentiles: tuple[float, float] = (1, 99), masking_fn: Callable | None = None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
VolumeTransformRescale intensities in a 3d volume to a given range.
It is robust to outliers since the volume is clipped according to a given inter-quantile range. It applies the following percentile-based min-max transformation per channel:
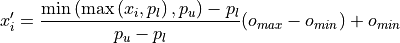

where :math:x_i is the original voxel intensity,
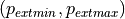 defines the input quantile range used for clipping, and
defines the input quantile range used for clipping, and
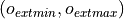 defines the target output
intensity range.
defines the target output
intensity range.It handles a
np.ndarrayortorch.Tensoras input and returns a consistent output (same type and shape). Input shape must be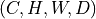 or
or 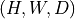 (spatial dimensions).
(spatial dimensions).- Parameters:
out_min_max : (float, float), default=(0, 1)
Range of output intensities.
percentiles : (float, float), default=(1, 99)
masking_fn : Callable or None, default=None
If Callable, a masking function returning a boolean mask to be applied on the input volume for each channel separately. Only voxels inside the mask are used to compute the cutoff values when clipping the data. If None, the whole volume is taken to compute the cutoff.
kwargs : dict
Keyword arguments given to
nidl.transforms.Transform.
Notes
If the input volume has constant values, the normalized output is set to its minimum value by convention.
References
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from nidl.volume.transforms import RobustRescaling >>> # Create a random 3d volume with shape (64, 64, 64) >>> volume = np.random.normal(loc=100, scale=20, size=(64, 64, 64)) >>> # Define the transform >>> transform = RobustRescaling(out_min_max=(0, 1), percentiles=(1, 99)) >>> # Apply the transform >>> rescaled = transform(volume) >>> rescaled.shape (64, 64, 64) >>> # Values are now in the range [0, 1] >>> rescaled.min(), rescaled.max() (0.0, 1.0)
Follow us
